INTERACTIVE DESIGN - LECTURES / EXERCISES
03/30/2022
Hansel Ribowo (0350008)
Advanced Typography
Exercises
LECTURE NOTES
Week 1
In week 1 we were briefed about the MIB and the projects that we need to do
in the next 13 weeks.
- Project 1 and Project 2 is related
- need to subscribe to netify.com
- will check the blog after each task is due
- every time need to upload the file, save it as index.html
- lower case only when we rename the file
- need to study on our own as well
Week 2
A website is a web document that is on the internet. One page or more,
these website has a different purpose.
Type of website
- Informational website
- Corporate website
- Portfolio website
- Brochure website
- Entertainment website
- Personal website
- Educational website
- E-commerce website
- Nonprofit website
Week 3
In week 3 we learn about how to add:
- Image
- Image Formats for web
- ID Attribute
- Class Attribute
In HTML by using Visual Studio Code or Dream Weaver.
Week 4
UI vs UX, Introduction to CSS
UX Designer
Focuses on the structure, layout, navigation, and how users
interact with the content. The things they produce includes
site-maps, user flows, prototypes and wireframes. They are more
focused on the underlying structure and purpose of the software or
webpage. Visual appearance does not have impacts on UX design,
instead it is only applied at the next stage after UX
design.
UI Designer
Focuses on anticipating what users might need to do when using a
software or webpage and ensure there are elements ready for them
to have ease of usage. Focus on how the functions of a webpage or
software are displayed and the details on how users interact with
the interface. They produce the visual comps and functioning
front-end code (HTML, CSS). Brings concepts from interaction
design, visual design and information architecture. UI design is
about the polished final production and quality outputs
stage
User interface design
Some interface elements includes:
- Input controls: button, text fields, checkboxes, dropdown lists, toggles, radio buttons, list boxes, date field
- Navigational components: breadcrumb, slider, search field, slider, tags, icons, pagination
- Informational components: icons, progress bar, notifications, tooltips, message boxes, modal windows
- Containers: accordion
Knowing what interface elements most users are familiar with
would help in creating an effective and satisfactory interface as
the interface should be predictable for the users.
Common characteristics of an effective design
First thing to consider is determining who the user is. The
design must be as broad or as narrow as possible to serve the
intended user. Listen to what your users need and observe them
interacting with your design, it is through this that the end
product of the design can actually be functionable and meet the
user's need.
Golden rules of interface design
- Ease of learning
- Efficiency of use
- Memorability
- Minimize errors
- Satisfy the users
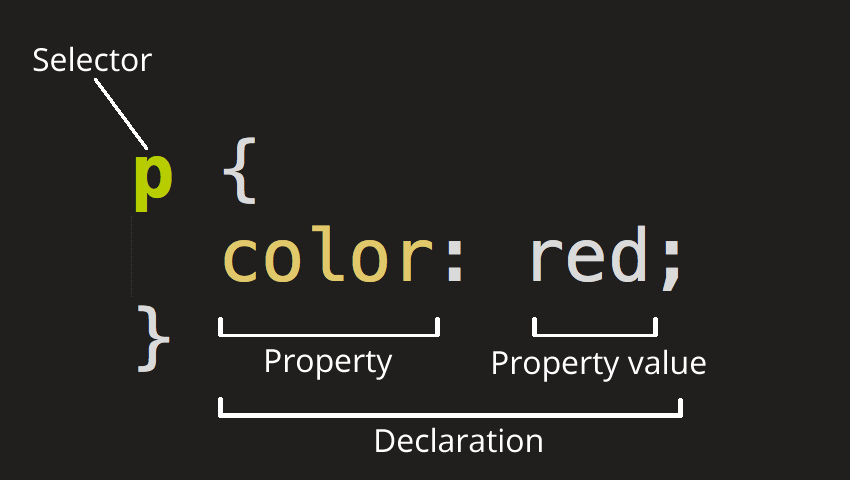
CSS (Cascading Style Sheet)
Used to specify how the content of an element appear in the
interface by creating rules. CSS works by associating its rules
with HTML elements. It contains a selector and a
declaration.
Selectors: indicate the element you want to apply
specific appearance on. There can be more than one element as the
selector.
Declaration: indicate how the elements in the
selectors should be styled. It is separated into two parts, a
property and a value, and are separated by a colon.
Property indicates the aspects that you want to change, and value
indicated the specific characteristic you want to apply to that
aspect. Declarations should also be in curly brackets.
e.g:
p, h1, h2, h3 {
font-family:Arial;
color: yellow;
Using external CSS
A <link> element can be used to tell a browser where to
find the external CSS file to be used to style the webpage. It
should also be in the <head> element. It contains three
attributes which are "href", "type", "rel". e.g:
<link href="style.css" type="text/css"
rel="stylesheet">
href-specify source path
type-specify the type of document, in this case, it should
be "text/css"
rel-specify the relationship between the source file and
the HTML file, in this case, it should be "stylesheet"
A HTML page can have more than one CSS style sheet, just include
multiple <link> element to link the external CSS
files.
Embedded style
Use <style> element to employ CSS codes within a HTML
document. It should also be within the <head> element. The
attribute "text/css" should also be included to specify that the
styles are in CSS.
Inline style
Internal CSS can also be used in line with HTML element by using
"style" as an attribute. e,g:
<li style="color: aqua"> blue </li>
A browser will read the inline style, and then the embedded
style, and finally the external CSS style sheet.
External CSS should be used when building a sire with more than
one page, this is because it allows all pages to use the same
style rules and allows you to change the content of the page
without interfering with the CSS rules and without having to edit
the CSS in each individual pages.
Week 5 and Week 7
Text style
font-weight
Allows you to control the weight of a text. Text appears in
normal weight when "normal" value is used, and bold when "bold"
value is used.
font-style
Allows you to control the style of a text. Values include
normal-text, italic, oblique.
text-transform
Used to change the case of a text. Values include uppercase,
lowercase, capitalise. The capitalise value only capitalise the
first letter of each word.
text-decoration
Adds additional formatting to the text. Values include none
(removes any decoration already applied to the text), underline,
overline (adds a line over the top of the text), line-through
(strikethrough).
text-indent
Creates indent to the first line of text within an element. It
allows you to control the amount of indentation by pixels or em,
it can also have negative values.
text-shadow
Used to create a drop shadow to a text. It has 4 values: x, y,
blur and colour
x
Controls how far the drop shadow it from the text
y
Controls the position of the shadow in the y-axis
blur
Controls the amont of blur of the drop shadow
color
Controls the colour of the drop shadow
text-align
Changes the alignment of a text. Values include right, left,
center, justify, inherit
CSS boxes model
CSS treats each HTML element as if they're in a box, and so, the
border, colour etc. of the box can be changed.
Box dimension – Width, Height
The dimension of the box can be adjusted by using width and
height properties, the widely most unit measurement are pixels or
percentage.
Limiting width and height
min-width, max-width, min-height, and max-height property can be
included to determine the minimum or maximum width or height of a
box. The minimum property limits the minimum size the box can be
when the window is narrow and the maximum property limits the
maximum size the box can be when the window is wide.
Overflowing content
The overflow property controls how the content in a box appears
when there is not enough space in the box for the content. The
overflow property can have the value of either hidden or
scroll.
Hidden - hides any extra content that does not fit
the box
Scroll - adds a scrollbar to the box so that users
can scroll to see the missing content
Border, margin and padding
Border, margin and padding of a box can also be adjusted in CSS.
Border indicates the edge of a box, while margin indicates the gap
between the edge of one box and the edge of the other. Padding
indicates the space between the border of the box and the content
inside the box. Adding padding can improve the readability of the
content in the box.
The Display Property
Every element in CSS has a default display value depending on its
type of element. The default property is often block or
inline.
Block-level element
The standard block-level element is <div>. This type of
element starts on a new line and stretches out to the left or
right as far as it can. Other common block-level elements are p,
form , header, section etc.
Inline element
<span> is the standard inline element. An inline element
can wrap text within a paragraph by using
"<span></span>" without destructing the flow of the
paragraph. Common inline element is <a>
The default display type can always be overridden for
customization purposes, for example, customizing the <li>
tag to look like a navigation bar.
Week 7 tutorial and practical class activity
During week 7 class, we followed along Mr. Shamsul to create a
basic webpage layout using CSS. Here are some of the extra notes
taken during class:
- <--word--> - used to add a comment in HTML script
- /*word*/ - used to add a comment in CSS script
- <nav> - add navigation
- Block element appearance on a site follows chronological order on how it appears in the HTML document
- When creating a responsive website, the value used must be relative, i.e: the unit needs to be in percentage.
- To select a class element from a HTML document in a CSS document, add "." in front of the class name.
- Refrain from using too much background colours when designing a website.
Instructions
Exercises
Week 1
Today in class, we form groups and find good and bad website from a website
that was given by Mr. Shamsul. Below are the website that me and my friends
found from the source.
Week 2 Exercise 1
Week 3 Exercise 2
Fig 1.6 Exercises Week 3
Exercise 3
Fig 1.9 Layout Exercise
Netlify Link : https://layoutexercise-hanselribowo.netlify.app
Feedback
-
Reflection
Reflection
In this exercise i really enjoy it because i can understand what the lecture say and i can keep up with the proses when doing the code.


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment